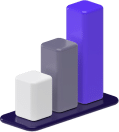When it comes to talking about value in the world of art, you might think that it means discussing the perceived cost of a painting or sculpture, but more often than not the word value refers to the lightness and darkness in a design or piece of art.
What is value contrast in art? Value contrast is the differences between light and dark in art. Value contrast can be used to draw the eye to a specific aspect, create stunning effects or the illusion of space, and illustrate a mood. Value contrast is only one of many forms of contrast often used in art for effect.
If you’ve ever felt confused about value contrast or color theory or wondered how knowledge of these concepts can make you a better artist, then this article is for you.
Here, you will learn about the different types of contrast in art, as well as how to effectively use value contrast and color theory in your own art.
Understanding Value Contrast & Color Theory in Art
In order to fully understand value contrast and color theory in art, it’s important to first comprehend some of the basic properties of color. These properties include:
- Hue: Hue refers to the colors of the visual spectrum. Hues can be combined to create all colors.
- Tint: If you add white to any hue, then the lighter color that results from the mixture is called a tint.
- Shade: A shade is the darker color that is created by adding black to any hue.
- Tone: A tone is created by adding gray to any color.
- Saturation or Intensity: Saturation refers to the brilliance or intensity of a color in relation to pure gray.
- Lightness: Lightness defines a color’s brightness.
- Chroma: Chroma is the component that determines the purity of a color.
What Is Contrast in Art?
Contrast in art refers to the intentional arrangement of opposing elements in order to create a visually appealing image.
Types of Contrast in Art
Types of contrast in art can include hue contrast, value contrast, saturation contrast, texture contrast, shape contrast, line contrast, size contrast, edge contrast, temperature contrast, and space contrast.
- Hue contrast can be created by choosing to use complementary colors in your art. Complementary colors are colors that are located opposite of each other on a color wheel, such as orange and blue.
- Value contrast is created when you choose to combine a lighter and a darker color. Using black and white is the easiest way to see the striking effect of value contrast.
- Saturation contrast is when you combine a brilliant color with a duller color.
- Texture contrast is created when you mix smooth and rough textures. Texture contrast is often used in crafts such as collaging, journaling, and making greeting cards.
- Shape contrast is when you combine different shapes to create eye-catching art. Many modern abstract artists use shape contrast in their art.
- Line contrast is created when you combine opposing lines in your art. This can be done through the use of lines of varying thickness and thinness as well as using different shapes of lines, from straight to curvy to wiggly.
- Size contrast is using smaller and larger objects to create striking effects in your art.
- Edge contrast is combining soft and hard edges in your artwork.
- Temperature contrast is created through the combination of warm and cool colors. Warm colors are colors like red, orange, and yellow, while cool colors are colors such as blue, green, and purple.
- Space contrast is the intentional use of blank space to create visual appeal.
The Importance of Contrast in Art
Using contrast in art creates an intriguing dynamic that mimics the duality of life. It can add drama or flair to a piece of art and can help you to draw attention to certain elements of your art.
Contrast can help you to tell a better story with your art by demonstrating a strong mood and can help the viewer to understand more clearly the intention of your piece.
Examples of Contrast in Art
Black-and-white photography is a very clear example of using value contrast in art.
The complete lack of other colors forces the eye to pay attention to the nuances of shadow and light, adding a three-dimensional depth to a two-dimensional artwork.
Another good example of contrast in art is the work of Vincent Van Gogh. He often used hue contrast to create his unforgettable works.
Value Contrast
Value contrast is the amount of difference in light and darkness between two elements.
Value contrast is an important concept in art, as it is used to create stunning effects that would not otherwise be possible.
Why Do Artists Use Value Contrast?
Artists use value contrast in order to create the illusion of space.
Painting a lighter object against a darker background can make the lighter object appear as if there is separation between the object and the background.
Artists can also use value contrast to guide the viewer’s eye to specific focal points as well as to determine a distinct mood in their artwork.
Color Theory
Color theory is a guide to color mixing and how different colors interact with each other and the effects they can create when combined.
A great way to learn about color theory is through the color wheel. The color wheel contains 12 different hues, which are divided into primary, secondary, and tertiary colors.
- Primary colors are those hues which can be mixed to create all other colors. The primary colors are red, yellow, and blue, and they are located three spaces away from each other on the color wheel.
- Secondary colors are created by mixing two of the primary colors and are also located three spaces away from each other on the color wheel. The secondary colors are orange, violet, and green.
- Tertiary colors are formed by combining a primary color with a secondary color. They’re located one space away from each other on the color wheel. The tertiary colors are yellow-green, blue-green, blue-violet, red-violet, red-orange, and yellow-orange.
The color wheel also contains the tints, shades, and tones of each of the 12 hues. The combination of a hue and its corresponding tint, shade, and tone is called a color family.
What Is Color Harmony?
Color harmony is combining colors in a way that is agreeable to the eye. Color harmony can easily be created by applying specific geometric shapes to the color wheel.
- Monochromatic harmony is created when using tints, tones, and shades from the same color family along with black, white, or gray.
- Diad harmony is created by combining two colors that are separated by one color on the color wheel, such as yellow-orange and yellow-green.
- Complementary harmony is when you combine complementary colors or two colors that are located directly opposite of each other on the color wheel.
- Split complementary harmony is formed by combining one color with the two colors directly to either side of the first color’s complementary color on the color wheel.
- Triad harmony is created when combining three colors that are equidistant from each other on the color wheel, such as red, yellow, and blue.
- Analogous harmony is formed when combining three colors that are next to each other on the color wheel.
- Double complementary is created when combining two colors that are right next to each other on the color wheel with their complementary colors.
Another important element of color theory is color context. Color context refers to the ways that a color can appear to look different based on the colors or shapes that surround it.
You may have seen optical illusions that show a seemingly different colored square against different colored backgrounds; when the background is removed the square is shown to actually be the same color.
Perhaps you remember the infamous dress photograph, where people from across the internet argued as to whether the dress was black and blue or white and gold.
You have color context to thank for that viral image.
Color context comes down to the idea that color is relative, and our perception of color is dependent on things such as values, saturations, and the warmth or coolness of surrounding colors.
How Value Contrast Relates to Color Theory
Value contrast shows the difference between light and dark colors.
Once you understand the basics of color theory, you can use the concept of value contrast to make harmonious color combinations that effectively draw the viewer’s eye to certain elements of your art.
How To Use Value Contrast and Color Effectively
By placing darker and lighter colors in strategic positions, you can create an intentional mood or bring attention to a desired focal point of your art.
For instance, if you were creating a painting of a sunset, you could paint a dark foreground to bring attention to a bright sunset in the background.
The dark foreground will make the sunset appear lighter as well as give the illusion of shadows beginning further from the sun.
What’s the Difference Between Value and Contrast in Art?
Value refers to the range of light and darkness between and including black and white.
It can help to create the illusion of depth, making artwork appear more three-dimensional. Contrast in art can include value contrast, hue contrast, and saturation contrast, among others.
- Value contrast is the contrast between light and dark colors. If you have a light yellow and a dark red, the light yellow will have a lighter value than the dark red.
- Hue contrast refers to differences in color. Complementary colors will have the strongest contrast and are often used in painting for that reason.
- Saturation contrast is the difference between brilliant and dull colors. In order to effectively use saturation contrast, you can combine a dull colored background with a vividly colored object in the foreground. This will help make the object “pop” out from the background.
How Do You Analyze Contrast in Art?
To analyze contrast in art, take yourself on a trip to your local art museum.
Pay attention to paintings or photographs that catch your eye, and ask yourself what exactly it is that drew you to the artwork.
Did the artist use value contrast? Perhaps they used a combination of different types of contrast, such as size and color contrast.
Take note of how different artists use contrast and what works well in some artworks and falls flat in others.
Another great way to analyze contrast in art is to practice it yourself. Once you have used contrast in your own artwork, you will be more likely to notice it in the artwork of others.
Why Is Color Contrast Important in Art?
Without color contrast, art runs the risk of appearing dull, muddy, and boring.
Unless the artist intentionally wishes to create that kind of mood with their artwork, those are all things that are best avoided.
Using color contrast is a great way to make your artwork more dramatic and exciting.
What Are Easy Ways To Show Contrast in Art?
Easy ways to show contrast in art include creating art with just black and white; using different textures, sizes, and shapes; and combining soft and sharp edges within the artwork.
You can try to use thick paint with your light colors and thin paint with your dark colors, or use rough textures in the foreground and smoother textures in the background.
You can also use detail work to create interesting contrasts. Try using more detail on items in the foreground and less detail, or broader, more gestural strokes in the background.
You can also choose one focal point of the artwork to apply detail to and leave the rest of the piece mostly detail free.
Experiment with different types of contrast and see which ones work best for you and your style of art.
Conclusion
Value contrast and color theory are two important tools that can help you to better understand and create more visually stunning art.
Once you know how to effectively use lighter and darker values and mix colors effectively, you will be able to take your art to a whole new level!
Source:
http://www.workwithcolor.com/color-properties-definitions-0101.htm